drift_detector
Expand source code
import sys import operator import functools import pyspark from loguru import logger from pyspark.sql import functions as F from pyspark.sql import types as T from pyspark.sql.window import Window from anovos.data_ingest.data_sampling import data_sample from anovos.data_transformer.transformers import attribute_binning from anovos.shared.utils import attributeType_segregation from .validations import check_distance_method, check_list_of_columns @check_distance_method @check_list_of_columns def statistics( spark, idf_target, idf_source, list_of_cols="all", drop_cols=None, method_type="PSI", bin_method="equal_range", bin_size=10, threshold=0.1, use_sampling=True, sample_method="random", strata_cols="all", stratified_type="population", sample_size=100000, sample_seed=42, persist=True, persist_option=pyspark.StorageLevel.MEMORY_AND_DISK, pre_existing_source=False, source_save=True, source_path="NA", model_directory="drift_statistics", print_impact=False, ): """ When the performance of a deployed machine learning model degrades in production, one potential reason is that the data used in training and prediction are not following the same distribution. Data drift mainly includes the following manifestations: - Covariate shift: training and test data follow different distributions. For example, An algorithm predicting income that is trained on younger population but tested on older population. - Prior probability shift: change of prior probability. For example in a spam classification problem, the proportion of spam emails changes from 0.2 in training data to 0.6 in testing data. - Concept shift: the distribution of the target variable changes given fixed input values. For example in the same spam classification problem, emails tagged as spam in training data are more likely to be tagged as non-spam in testing data. In our module, we mainly focus on covariate shift detection. In summary, given 2 datasets, source and target datasets, we would like to quantify the drift of some numerical attributes from source to target datasets. The whole process can be broken down into 2 steps: (1) convert each attribute of interest in source and target datasets into source and target probability distributions. (2) calculate the statistical distance between source and target distributions for each attribute. In the first step, attribute_binning is firstly performed to bin the numerical attributes of the source dataset, which requires two input variables: bin_method and bin_size. The same binning method is applied on the target dataset to align two results. The probability distributions are computed by dividing the frequency of each bin by the total frequency. In the second step, 4 choices of statistical metrics are provided to measure the data drift of an attribute from source to target distribution: Population Stability Index (PSI), Jensen-Shannon Divergence (JSD), Hellinger Distance (HD) and Kolmogorov-Smirnov Distance (KS). They are calculated as below: For two discrete probability distributions *P=(p_1,…,p_k)* and *Q=(q_1,…,q_k),* 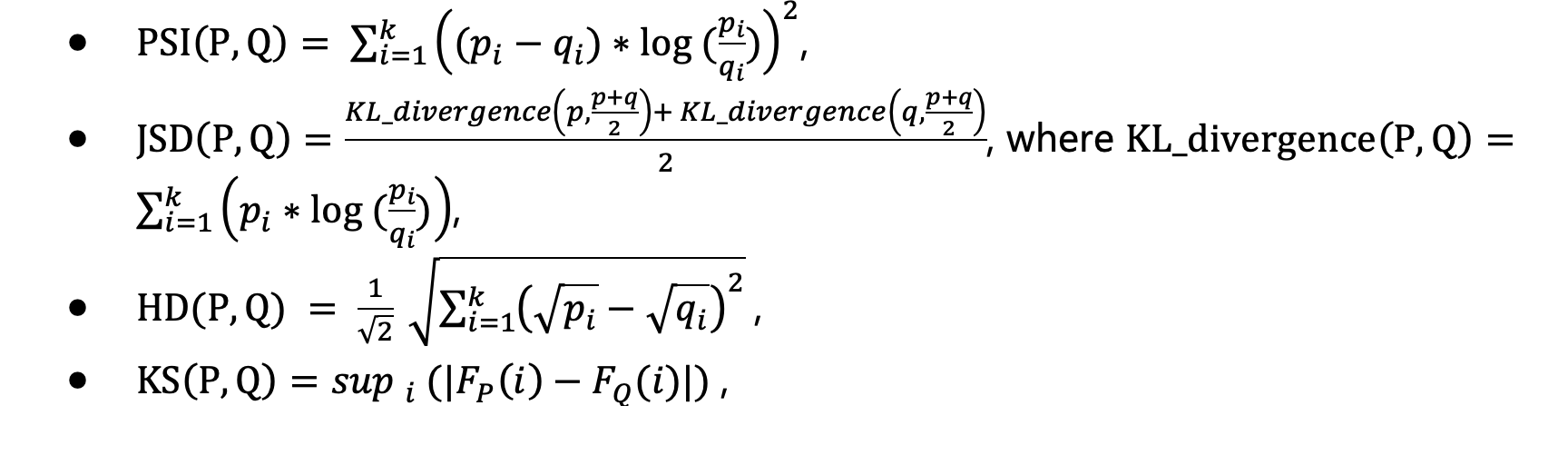 A threshold can be set to flag out drifted attributes. If multiple statistical metrics have been calculated, an attribute will be marked as drifted if any of its statistical metric is larger than the threshold. This function can be used in many scenarios. For example: 1. Attribute level data drift can be analysed together with the attribute importance of a machine learning model. The more important an attribute is, the more attention it needs to be given if drift presents. 2. To analyse data drift over time, one can treat one dataset as the source / baseline dataset and multiple datasets as the target datasets. Drift analysis can be performed between the source dataset and each of the target dataset to quantify the drift over time. Parameters ---------- spark Spark Session idf_target Input Dataframe idf_source Baseline/Source Dataframe. This argument is ignored if pre_existing_source is True. list_of_cols List of columns to check drift e.g., ["col1","col2"]. Alternatively, columns can be specified in a string format, where different column names are separated by pipe delimiter “|” e.g., "col1|col2". "all" can be passed to include all (non-array) columns for analysis. Please note that this argument is used in conjunction with drop_cols i.e. a column mentioned in drop_cols argument is not considered for analysis even if it is mentioned in list_of_cols. (Default value = "all") drop_cols List of columns to be dropped e.g., ["col1","col2"]. Alternatively, columns can be specified in a string format, where different column names are separated by pipe delimiter “|” e.g., "col1|col2". (Default value = None) method_type "PSI", "JSD", "HD", "KS","all". "all" can be passed to calculate all drift metrics. One or more methods can be passed in a form of list or string where different metrics are separated by pipe delimiter “|” e.g. ["PSI", "JSD"] or "PSI|JSD". (Default value = "PSI") bin_method String argument - "equal_frequency" or "equal_range". In "equal_range" method, each bin is of equal size/width and in "equal_frequency", each bin has equal no. of rows, though the width of bins may vary. (Default value = "equal_range") bin_size Integer argument - Number of bins for creating histogram. (Default value = 10) threshold Float argument - A column is flagged if any drift metric is above the threshold. (Default value = 0.1) use_sampling Boolean argument - True or False. This argument is used to determine whether to use random sample method on source and target dataset, True will enable the use of sample method, otherwise False. It is recommended to set this as True for large datasets. (Default value = True) sample_method String argument - "random" or "stratified". If use_sampling is True, this argument is used to determine the sampling method. "stratified" for Stratified sampling, "random" for Random Sampling. For more details, please refer to https://docs.anovos.ai/api/data_ingest/data_sampling.html. (Default value = "random") strata_cols If use_sampling is True and sample_method is "stratified", this argument is used to determine the list of columns used to be treated as strata. For more details, please refer to https://docs.anovos.ai/api/data_ingest/data_sampling.html. (Default value = "all") stratified_type String argument - "population" or "balanced". If use_sampling is True and sample_method is "stratified", this string argument is used to determine the stratified sampling method. "population" stands for Proportionate Stratified Sampling, "balanced" stands for Optimum Stratified Sampling. For more details, please refer to https://docs.anovos.ai/api/data_ingest/data_sampling.html. (Default value = "population") sample_size Integer argument - If use_sampling is True, this argument is used to determine the sample size of sampling method. (Default value = 100000) sample_seed Integer argument - If use_sampling is True, this argument is used to determine the seed of sampling method. (Default value = 42) persist Boolean argument - True or False. This argument is used to determine whether to persist on binning result of source and target dataset, True will enable the use of persist, otherwise False. It is recommended to set this as True for large datasets. (Default value = True) persist_option If persist is True, this argument is used to determine the type of persist. (Default value = pyspark.StorageLevel.MEMORY_AND_DISK) pre_existing_source Boolean argument – True or False. True if the drift_statistics folder (binning model & frequency counts for each attribute) exists already, False Otherwise. (Default value = False) source_save Boolean argument - True or False. This argument will determine whether or not to save the source to source_path. (Default value = False) source_path If pre_existing_source is False, this argument can be used for saving the drift_statistics folder. The drift_statistics folder will have attribute_binning (binning model) & frequency_counts sub-folders. If pre_existing_source is True, this argument is path for referring the drift_statistics folder. Default "NA" for temporarily saving data in "intermediate_data/" folder. (Default value = "NA") model_directory If pre_existing_source is False, this argument can be used for saving the drift stats to folder. The default drift statics directory is drift_statistics folder will have attribute_binning If pre_existing_source is True, this argument is model_directory for referring the drift statistics dir. Default "drift_statistics" for temporarily saving source dataset attribute_binning folder. (Default value = "drift_statistics") print_impact Boolean argument - True or False. This argument is to print out the drift statistics of all attributes and attributes meeting the threshold. (Default value = False) Returns ------- DataFrame [attribute, *metric, flagged] Number of columns will be dependent on method argument. There will be one column for each drift method/metric. """ drop_cols = drop_cols or [] num_cols = attributeType_segregation(idf_target.select(list_of_cols))[0] count_target = idf_target.count() count_source = idf_source.count() if use_sampling: if count_target > sample_size: idf_target = data_sample( idf_target, strata_cols=strata_cols, fraction=sample_size / count_target, method_type=sample_method, stratified_type=stratified_type, seed_value=sample_seed, ) if persist: idf_target = idf_target.persist(persist_option) count_target = idf_target.count() if count_source > sample_size: idf_source = data_sample( idf_source, strata_cols=strata_cols, fraction=sample_size / count_source, method_type=sample_method, stratified_type=stratified_type, seed_value=sample_seed, ) if persist: idf_source = idf_source.persist(persist_option) count_source = idf_source.count() if source_path == "NA": source_path = "intermediate_data" if not pre_existing_source: source_bin = attribute_binning( spark, idf_source, list_of_cols=num_cols, method_type=bin_method, bin_size=bin_size, pre_existing_model=False, model_path=source_path + "/" + model_directory, ) if persist: source_bin = source_bin.persist(persist_option) target_bin = attribute_binning( spark, idf_target, list_of_cols=num_cols, method_type=bin_method, bin_size=bin_size, pre_existing_model=True, model_path=source_path + "/" + model_directory, ) if persist: target_bin = target_bin.persist(persist_option) temp_list = [] for i in list_of_cols: temp_method_join_list = [] if pre_existing_source: x = spark.read.csv( source_path + "/" + model_directory + "/frequency_counts/" + i, header=True, inferSchema=True, ) else: x = ( source_bin.groupBy(i) .agg((F.count(i) / count_source).alias("p")) .fillna(-1) ) if source_save: x.coalesce(1).write.csv( source_path + "/" + model_directory + "/frequency_counts/" + i, header=True, mode="overwrite", ) y = target_bin.groupBy(i).agg((F.count(i) / count_target).alias("q")).fillna(-1) xy = ( x.join(y, i, "full_outer") .fillna(0.0001, subset=["p", "q"]) .replace(0, 0.0001) .orderBy(i) ) if "PSI" in method_type: xy_psi = ( xy.withColumn( "deduct_ln_mul", ((F.col("p") - F.col("q")) * (F.log(F.col("p") / F.col("q")))), ) .select(F.sum(F.col("deduct_ln_mul")).alias("PSI")) .withColumn("attribute", F.lit(str(i))) .select("attribute", "PSI") ) temp_method_join_list.append(xy_psi) if "HD" in method_type: xy_hd = ( xy.withColumn( "pow", F.pow((F.sqrt(F.col("p")) - F.sqrt(F.col("q"))), 2), ) .select(F.sqrt(F.sum(F.col("pow")) / 2).alias("HD")) .withColumn("attribute", F.lit(str(i))) .select("attribute", "HD") ) temp_method_join_list.append(xy_hd) if "JSD" in method_type: xy_jsd = ( xy.withColumn("m", ((F.col("p") + F.col("q")) / 2)) .withColumn("log_pm", (F.col("p") * F.log(F.col("p") / F.col("m")))) .withColumn("log_qm", (F.col("q") * F.log(F.col("q") / F.col("m")))) .select( F.sum(F.col("log_pm")).alias("pm"), F.sum(F.col("log_qm")).alias("qm"), ) .select(((F.col("pm") + F.col("qm")) / 2).alias("JSD")) .withColumn("attribute", F.lit(str(i))) .select("attribute", "JSD") ) temp_method_join_list.append(xy_jsd) if "KS" in method_type: xy_ks = ( xy.withColumn( "cum_sum_p", F.sum(F.col("p")).over( Window.partitionBy().orderBy().rowsBetween(-sys.maxsize, 0) ), ) .withColumn( "cum_sum_q", F.sum(F.col("q")).over( Window.partitionBy().orderBy().rowsBetween(-sys.maxsize, 0) ), ) .withColumn( "deduct_abs", F.abs(F.col("cum_sum_p") - F.col("cum_sum_q")) ) .select( F.max(F.col("deduct_abs")).alias("KS"), ) .withColumn("attribute", F.lit(str(i))) .select("attribute", "KS") ) temp_method_join_list.append(xy_ks) xy_temp = temp_method_join_list[0] if len(temp_method_join_list) > 1: for count in range(1, len(temp_method_join_list)): xy_temp = xy_temp.join( temp_method_join_list[count], "attribute", "inner" ) temp_list.append(xy_temp) def unionAll(dfs): first, *_ = dfs return first.sql_ctx.createDataFrame( first.sql_ctx._sc.union([df.rdd for df in dfs]), first.schema ) odf_union = unionAll(temp_list) cond_expr = functools.reduce( operator.or_, [(F.col(c) > threshold) for c in odf_union.columns[1:]] ) odf = odf_union.withColumn("flagged", F.when(cond_expr, 1).otherwise(0)) if print_impact: logger.info("All Attributes:") odf.show(len(list_of_cols)) logger.info("Attributes meeting Data Drift threshold:") drift = odf.where(F.col("flagged") == 1) drift.show(drift.count()) if persist: idf_target.unpersist() idf_source.unpersist() if not pre_existing_source: source_bin.unpersist() target_bin.unpersist() return odf
Functions
def statistics(spark, idf_target, idf_source, list_of_cols='all', drop_cols=None, method_type='PSI', bin_method='equal_range', bin_size=10, threshold=0.1, use_sampling=True, sample_method='random', strata_cols='all', stratified_type='population', sample_size=100000, sample_seed=42, persist=True, persist_option=StorageLevel(True, True, False, False, 1), pre_existing_source=False, source_save=True, source_path='NA', model_directory='drift_statistics', print_impact=False)-
When the performance of a deployed machine learning model degrades in production, one potential reason is that the data used in training and prediction are not following the same distribution.
Data drift mainly includes the following manifestations:
- Covariate shift: training and test data follow different distributions. For example, An algorithm predicting income that is trained on younger population but tested on older population.
- Prior probability shift: change of prior probability. For example in a spam classification problem, the proportion of spam emails changes from 0.2 in training data to 0.6 in testing data.
- Concept shift: the distribution of the target variable changes given fixed input values. For example in the same spam classification problem, emails tagged as spam in training data are more likely to be tagged as non-spam in testing data.
In our module, we mainly focus on covariate shift detection.
In summary, given 2 datasets, source and target datasets, we would like to quantify the drift of some numerical attributes from source to target datasets. The whole process can be broken down into 2 steps: (1) convert each attribute of interest in source and target datasets into source and target probability distributions. (2) calculate the statistical distance between source and target distributions for each attribute.
In the first step, attribute_binning is firstly performed to bin the numerical attributes of the source dataset, which requires two input variables: bin_method and bin_size. The same binning method is applied on the target dataset to align two results. The probability distributions are computed by dividing the frequency of each bin by the total frequency.
In the second step, 4 choices of statistical metrics are provided to measure the data drift of an attribute from source to target distribution: Population Stability Index (PSI), Jensen-Shannon Divergence (JSD), Hellinger Distance (HD) and Kolmogorov-Smirnov Distance (KS).
They are calculated as below: For two discrete probability distributions P=(p_1,…,p_k) and Q=(q_1,…,q_k),
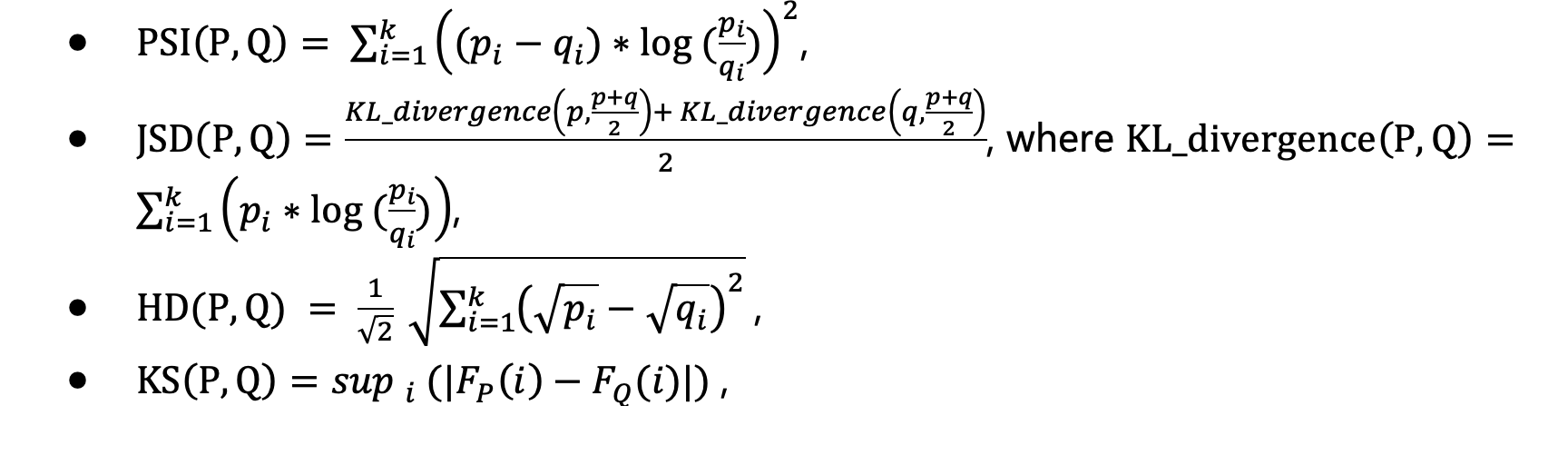
A threshold can be set to flag out drifted attributes. If multiple statistical metrics have been calculated, an attribute will be marked as drifted if any of its statistical metric is larger than the threshold.
This function can be used in many scenarios. For example:
- Attribute level data drift can be analysed together with the attribute importance of a machine learning model. The more important an attribute is, the more attention it needs to be given if drift presents.
- To analyse data drift over time, one can treat one dataset as the source / baseline dataset and multiple datasets as the target datasets. Drift analysis can be performed between the source dataset and each of the target dataset to quantify the drift over time.
Parameters
spark- Spark Session
idf_target- Input Dataframe
idf_source- Baseline/Source Dataframe. This argument is ignored if pre_existing_source is True.
list_of_cols- List of columns to check drift e.g., ["col1","col2"]. Alternatively, columns can be specified in a string format, where different column names are separated by pipe delimiter “|” e.g., "col1|col2". "all" can be passed to include all (non-array) columns for analysis. Please note that this argument is used in conjunction with drop_cols i.e. a column mentioned in drop_cols argument is not considered for analysis even if it is mentioned in list_of_cols. (Default value = "all")
drop_cols- List of columns to be dropped e.g., ["col1","col2"]. Alternatively, columns can be specified in a string format, where different column names are separated by pipe delimiter “|” e.g., "col1|col2". (Default value = None)
method_type- "PSI", "JSD", "HD", "KS","all". "all" can be passed to calculate all drift metrics. One or more methods can be passed in a form of list or string where different metrics are separated by pipe delimiter “|” e.g. ["PSI", "JSD"] or "PSI|JSD". (Default value = "PSI")
bin_method- String argument - "equal_frequency" or "equal_range". In "equal_range" method, each bin is of equal size/width and in "equal_frequency", each bin has equal no. of rows, though the width of bins may vary. (Default value = "equal_range")
bin_size- Integer argument - Number of bins for creating histogram. (Default value = 10)
threshold- Float argument - A column is flagged if any drift metric is above the threshold. (Default value = 0.1)
use_sampling- Boolean argument - True or False. This argument is used to determine whether to use random sample method on source and target dataset, True will enable the use of sample method, otherwise False. It is recommended to set this as True for large datasets. (Default value = True)
sample_method- String argument - "random" or "stratified". If use_sampling is True, this argument is used to determine the sampling method. "stratified" for Stratified sampling, "random" for Random Sampling. For more details, please refer to https://docs.anovos.ai/api/data_ingest/data_sampling.html. (Default value = "random")
strata_cols- If use_sampling is True and sample_method is "stratified", this argument is used to determine the list of columns used to be treated as strata. For more details, please refer to https://docs.anovos.ai/api/data_ingest/data_sampling.html. (Default value = "all")
stratified_type- String argument - "population" or "balanced". If use_sampling is True and sample_method is "stratified", this string argument is used to determine the stratified sampling method. "population" stands for Proportionate Stratified Sampling, "balanced" stands for Optimum Stratified Sampling. For more details, please refer to https://docs.anovos.ai/api/data_ingest/data_sampling.html. (Default value = "population")
sample_size- Integer argument - If use_sampling is True, this argument is used to determine the sample size of sampling method. (Default value = 100000)
sample_seed- Integer argument - If use_sampling is True, this argument is used to determine the seed of sampling method. (Default value = 42)
persist- Boolean argument - True or False. This argument is used to determine whether to persist on binning result of source and target dataset, True will enable the use of persist, otherwise False. It is recommended to set this as True for large datasets. (Default value = True)
persist_option- If persist is True, this argument is used to determine the type of persist. (Default value = pyspark.StorageLevel.MEMORY_AND_DISK)
pre_existing_source- Boolean argument – True or False. True if the drift_statistics folder (binning model & frequency counts for each attribute) exists already, False Otherwise. (Default value = False)
source_save- Boolean argument - True or False. This argument will determine whether or not to save the source to source_path. (Default value = False)
source_path- If pre_existing_source is False, this argument can be used for saving the drift_statistics folder. The drift_statistics folder will have attribute_binning (binning model) & frequency_counts sub-folders. If pre_existing_source is True, this argument is path for referring the drift_statistics folder. Default "NA" for temporarily saving data in "intermediate_data/" folder. (Default value = "NA")
model_directory- If pre_existing_source is False, this argument can be used for saving the drift stats to folder. The default drift statics directory is drift_statistics folder will have attribute_binning If pre_existing_source is True, this argument is model_directory for referring the drift statistics dir. Default "drift_statistics" for temporarily saving source dataset attribute_binning folder. (Default value = "drift_statistics")
print_impact- Boolean argument - True or False. This argument is to print out the drift statistics of all attributes and attributes meeting the threshold. (Default value = False)
Returns
DataFrame- [attribute, *metric, flagged] Number of columns will be dependent on method argument. There will be one column for each drift method/metric.
Expand source code
@check_distance_method @check_list_of_columns def statistics( spark, idf_target, idf_source, list_of_cols="all", drop_cols=None, method_type="PSI", bin_method="equal_range", bin_size=10, threshold=0.1, use_sampling=True, sample_method="random", strata_cols="all", stratified_type="population", sample_size=100000, sample_seed=42, persist=True, persist_option=pyspark.StorageLevel.MEMORY_AND_DISK, pre_existing_source=False, source_save=True, source_path="NA", model_directory="drift_statistics", print_impact=False, ): """ When the performance of a deployed machine learning model degrades in production, one potential reason is that the data used in training and prediction are not following the same distribution. Data drift mainly includes the following manifestations: - Covariate shift: training and test data follow different distributions. For example, An algorithm predicting income that is trained on younger population but tested on older population. - Prior probability shift: change of prior probability. For example in a spam classification problem, the proportion of spam emails changes from 0.2 in training data to 0.6 in testing data. - Concept shift: the distribution of the target variable changes given fixed input values. For example in the same spam classification problem, emails tagged as spam in training data are more likely to be tagged as non-spam in testing data. In our module, we mainly focus on covariate shift detection. In summary, given 2 datasets, source and target datasets, we would like to quantify the drift of some numerical attributes from source to target datasets. The whole process can be broken down into 2 steps: (1) convert each attribute of interest in source and target datasets into source and target probability distributions. (2) calculate the statistical distance between source and target distributions for each attribute. In the first step, attribute_binning is firstly performed to bin the numerical attributes of the source dataset, which requires two input variables: bin_method and bin_size. The same binning method is applied on the target dataset to align two results. The probability distributions are computed by dividing the frequency of each bin by the total frequency. In the second step, 4 choices of statistical metrics are provided to measure the data drift of an attribute from source to target distribution: Population Stability Index (PSI), Jensen-Shannon Divergence (JSD), Hellinger Distance (HD) and Kolmogorov-Smirnov Distance (KS). They are calculated as below: For two discrete probability distributions *P=(p_1,…,p_k)* and *Q=(q_1,…,q_k),* 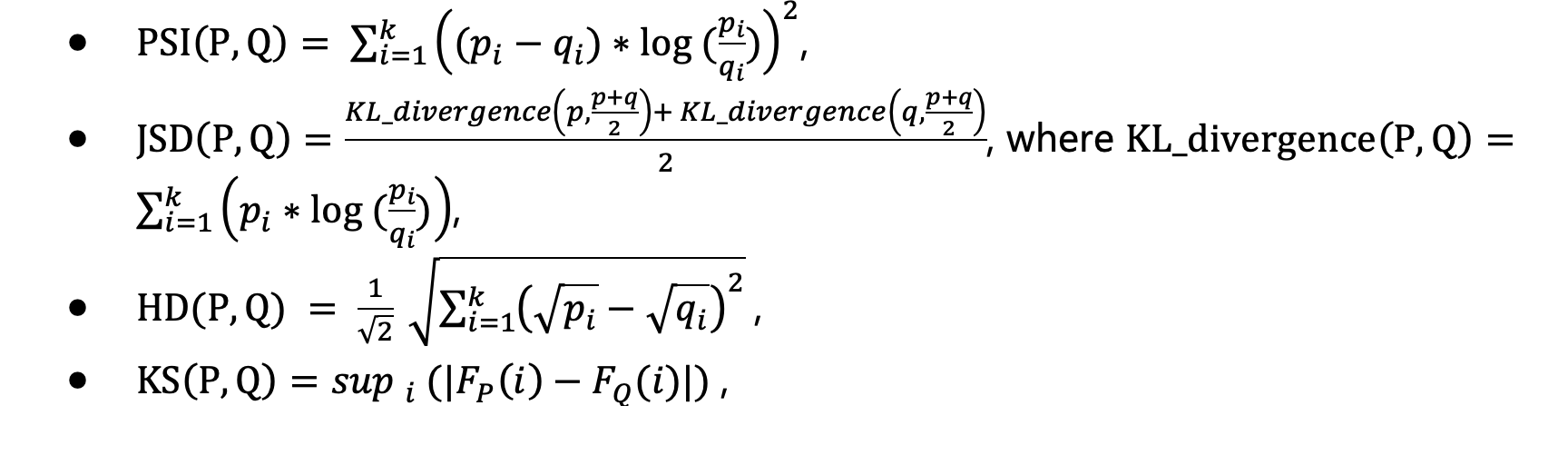 A threshold can be set to flag out drifted attributes. If multiple statistical metrics have been calculated, an attribute will be marked as drifted if any of its statistical metric is larger than the threshold. This function can be used in many scenarios. For example: 1. Attribute level data drift can be analysed together with the attribute importance of a machine learning model. The more important an attribute is, the more attention it needs to be given if drift presents. 2. To analyse data drift over time, one can treat one dataset as the source / baseline dataset and multiple datasets as the target datasets. Drift analysis can be performed between the source dataset and each of the target dataset to quantify the drift over time. Parameters ---------- spark Spark Session idf_target Input Dataframe idf_source Baseline/Source Dataframe. This argument is ignored if pre_existing_source is True. list_of_cols List of columns to check drift e.g., ["col1","col2"]. Alternatively, columns can be specified in a string format, where different column names are separated by pipe delimiter “|” e.g., "col1|col2". "all" can be passed to include all (non-array) columns for analysis. Please note that this argument is used in conjunction with drop_cols i.e. a column mentioned in drop_cols argument is not considered for analysis even if it is mentioned in list_of_cols. (Default value = "all") drop_cols List of columns to be dropped e.g., ["col1","col2"]. Alternatively, columns can be specified in a string format, where different column names are separated by pipe delimiter “|” e.g., "col1|col2". (Default value = None) method_type "PSI", "JSD", "HD", "KS","all". "all" can be passed to calculate all drift metrics. One or more methods can be passed in a form of list or string where different metrics are separated by pipe delimiter “|” e.g. ["PSI", "JSD"] or "PSI|JSD". (Default value = "PSI") bin_method String argument - "equal_frequency" or "equal_range". In "equal_range" method, each bin is of equal size/width and in "equal_frequency", each bin has equal no. of rows, though the width of bins may vary. (Default value = "equal_range") bin_size Integer argument - Number of bins for creating histogram. (Default value = 10) threshold Float argument - A column is flagged if any drift metric is above the threshold. (Default value = 0.1) use_sampling Boolean argument - True or False. This argument is used to determine whether to use random sample method on source and target dataset, True will enable the use of sample method, otherwise False. It is recommended to set this as True for large datasets. (Default value = True) sample_method String argument - "random" or "stratified". If use_sampling is True, this argument is used to determine the sampling method. "stratified" for Stratified sampling, "random" for Random Sampling. For more details, please refer to https://docs.anovos.ai/api/data_ingest/data_sampling.html. (Default value = "random") strata_cols If use_sampling is True and sample_method is "stratified", this argument is used to determine the list of columns used to be treated as strata. For more details, please refer to https://docs.anovos.ai/api/data_ingest/data_sampling.html. (Default value = "all") stratified_type String argument - "population" or "balanced". If use_sampling is True and sample_method is "stratified", this string argument is used to determine the stratified sampling method. "population" stands for Proportionate Stratified Sampling, "balanced" stands for Optimum Stratified Sampling. For more details, please refer to https://docs.anovos.ai/api/data_ingest/data_sampling.html. (Default value = "population") sample_size Integer argument - If use_sampling is True, this argument is used to determine the sample size of sampling method. (Default value = 100000) sample_seed Integer argument - If use_sampling is True, this argument is used to determine the seed of sampling method. (Default value = 42) persist Boolean argument - True or False. This argument is used to determine whether to persist on binning result of source and target dataset, True will enable the use of persist, otherwise False. It is recommended to set this as True for large datasets. (Default value = True) persist_option If persist is True, this argument is used to determine the type of persist. (Default value = pyspark.StorageLevel.MEMORY_AND_DISK) pre_existing_source Boolean argument – True or False. True if the drift_statistics folder (binning model & frequency counts for each attribute) exists already, False Otherwise. (Default value = False) source_save Boolean argument - True or False. This argument will determine whether or not to save the source to source_path. (Default value = False) source_path If pre_existing_source is False, this argument can be used for saving the drift_statistics folder. The drift_statistics folder will have attribute_binning (binning model) & frequency_counts sub-folders. If pre_existing_source is True, this argument is path for referring the drift_statistics folder. Default "NA" for temporarily saving data in "intermediate_data/" folder. (Default value = "NA") model_directory If pre_existing_source is False, this argument can be used for saving the drift stats to folder. The default drift statics directory is drift_statistics folder will have attribute_binning If pre_existing_source is True, this argument is model_directory for referring the drift statistics dir. Default "drift_statistics" for temporarily saving source dataset attribute_binning folder. (Default value = "drift_statistics") print_impact Boolean argument - True or False. This argument is to print out the drift statistics of all attributes and attributes meeting the threshold. (Default value = False) Returns ------- DataFrame [attribute, *metric, flagged] Number of columns will be dependent on method argument. There will be one column for each drift method/metric. """ drop_cols = drop_cols or [] num_cols = attributeType_segregation(idf_target.select(list_of_cols))[0] count_target = idf_target.count() count_source = idf_source.count() if use_sampling: if count_target > sample_size: idf_target = data_sample( idf_target, strata_cols=strata_cols, fraction=sample_size / count_target, method_type=sample_method, stratified_type=stratified_type, seed_value=sample_seed, ) if persist: idf_target = idf_target.persist(persist_option) count_target = idf_target.count() if count_source > sample_size: idf_source = data_sample( idf_source, strata_cols=strata_cols, fraction=sample_size / count_source, method_type=sample_method, stratified_type=stratified_type, seed_value=sample_seed, ) if persist: idf_source = idf_source.persist(persist_option) count_source = idf_source.count() if source_path == "NA": source_path = "intermediate_data" if not pre_existing_source: source_bin = attribute_binning( spark, idf_source, list_of_cols=num_cols, method_type=bin_method, bin_size=bin_size, pre_existing_model=False, model_path=source_path + "/" + model_directory, ) if persist: source_bin = source_bin.persist(persist_option) target_bin = attribute_binning( spark, idf_target, list_of_cols=num_cols, method_type=bin_method, bin_size=bin_size, pre_existing_model=True, model_path=source_path + "/" + model_directory, ) if persist: target_bin = target_bin.persist(persist_option) temp_list = [] for i in list_of_cols: temp_method_join_list = [] if pre_existing_source: x = spark.read.csv( source_path + "/" + model_directory + "/frequency_counts/" + i, header=True, inferSchema=True, ) else: x = ( source_bin.groupBy(i) .agg((F.count(i) / count_source).alias("p")) .fillna(-1) ) if source_save: x.coalesce(1).write.csv( source_path + "/" + model_directory + "/frequency_counts/" + i, header=True, mode="overwrite", ) y = target_bin.groupBy(i).agg((F.count(i) / count_target).alias("q")).fillna(-1) xy = ( x.join(y, i, "full_outer") .fillna(0.0001, subset=["p", "q"]) .replace(0, 0.0001) .orderBy(i) ) if "PSI" in method_type: xy_psi = ( xy.withColumn( "deduct_ln_mul", ((F.col("p") - F.col("q")) * (F.log(F.col("p") / F.col("q")))), ) .select(F.sum(F.col("deduct_ln_mul")).alias("PSI")) .withColumn("attribute", F.lit(str(i))) .select("attribute", "PSI") ) temp_method_join_list.append(xy_psi) if "HD" in method_type: xy_hd = ( xy.withColumn( "pow", F.pow((F.sqrt(F.col("p")) - F.sqrt(F.col("q"))), 2), ) .select(F.sqrt(F.sum(F.col("pow")) / 2).alias("HD")) .withColumn("attribute", F.lit(str(i))) .select("attribute", "HD") ) temp_method_join_list.append(xy_hd) if "JSD" in method_type: xy_jsd = ( xy.withColumn("m", ((F.col("p") + F.col("q")) / 2)) .withColumn("log_pm", (F.col("p") * F.log(F.col("p") / F.col("m")))) .withColumn("log_qm", (F.col("q") * F.log(F.col("q") / F.col("m")))) .select( F.sum(F.col("log_pm")).alias("pm"), F.sum(F.col("log_qm")).alias("qm"), ) .select(((F.col("pm") + F.col("qm")) / 2).alias("JSD")) .withColumn("attribute", F.lit(str(i))) .select("attribute", "JSD") ) temp_method_join_list.append(xy_jsd) if "KS" in method_type: xy_ks = ( xy.withColumn( "cum_sum_p", F.sum(F.col("p")).over( Window.partitionBy().orderBy().rowsBetween(-sys.maxsize, 0) ), ) .withColumn( "cum_sum_q", F.sum(F.col("q")).over( Window.partitionBy().orderBy().rowsBetween(-sys.maxsize, 0) ), ) .withColumn( "deduct_abs", F.abs(F.col("cum_sum_p") - F.col("cum_sum_q")) ) .select( F.max(F.col("deduct_abs")).alias("KS"), ) .withColumn("attribute", F.lit(str(i))) .select("attribute", "KS") ) temp_method_join_list.append(xy_ks) xy_temp = temp_method_join_list[0] if len(temp_method_join_list) > 1: for count in range(1, len(temp_method_join_list)): xy_temp = xy_temp.join( temp_method_join_list[count], "attribute", "inner" ) temp_list.append(xy_temp) def unionAll(dfs): first, *_ = dfs return first.sql_ctx.createDataFrame( first.sql_ctx._sc.union([df.rdd for df in dfs]), first.schema ) odf_union = unionAll(temp_list) cond_expr = functools.reduce( operator.or_, [(F.col(c) > threshold) for c in odf_union.columns[1:]] ) odf = odf_union.withColumn("flagged", F.when(cond_expr, 1).otherwise(0)) if print_impact: logger.info("All Attributes:") odf.show(len(list_of_cols)) logger.info("Attributes meeting Data Drift threshold:") drift = odf.where(F.col("flagged") == 1) drift.show(drift.count()) if persist: idf_target.unpersist() idf_source.unpersist() if not pre_existing_source: source_bin.unpersist() target_bin.unpersist() return odf